(논문 요약) Efficient Memory Management for Large Language Model Serving with PagedAttention
핵심 내용
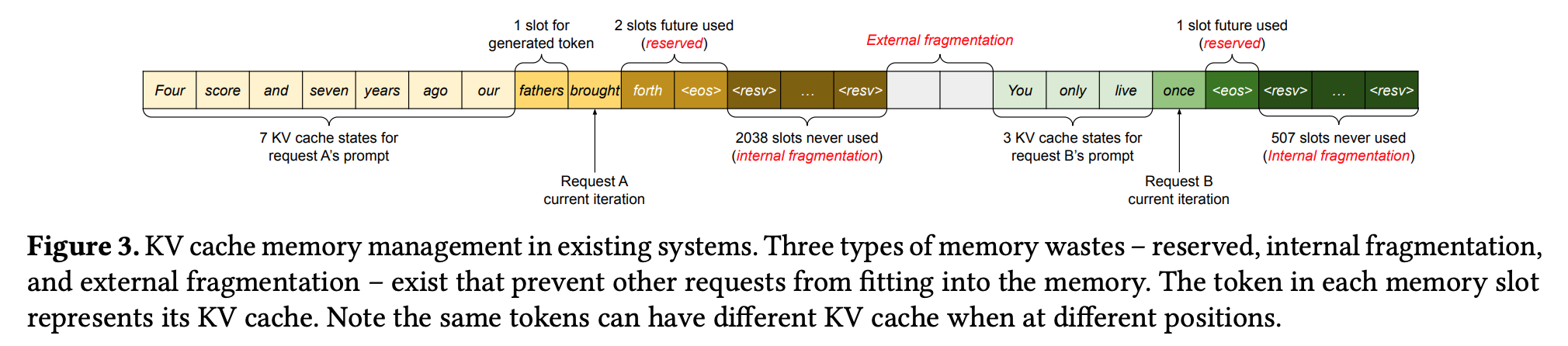
- 기존 시스템의 문제: fragmentation
- internal fragmentation: max length (e.g. 2048) 혹은 fixed size 만큼 contiguous memory chunk 가 pre-allocate 됨.
- external fragmentation: pre-allocated chunk 가 다양한 사이즈로 존재하여, 사용하지 않는 메모리 발생.
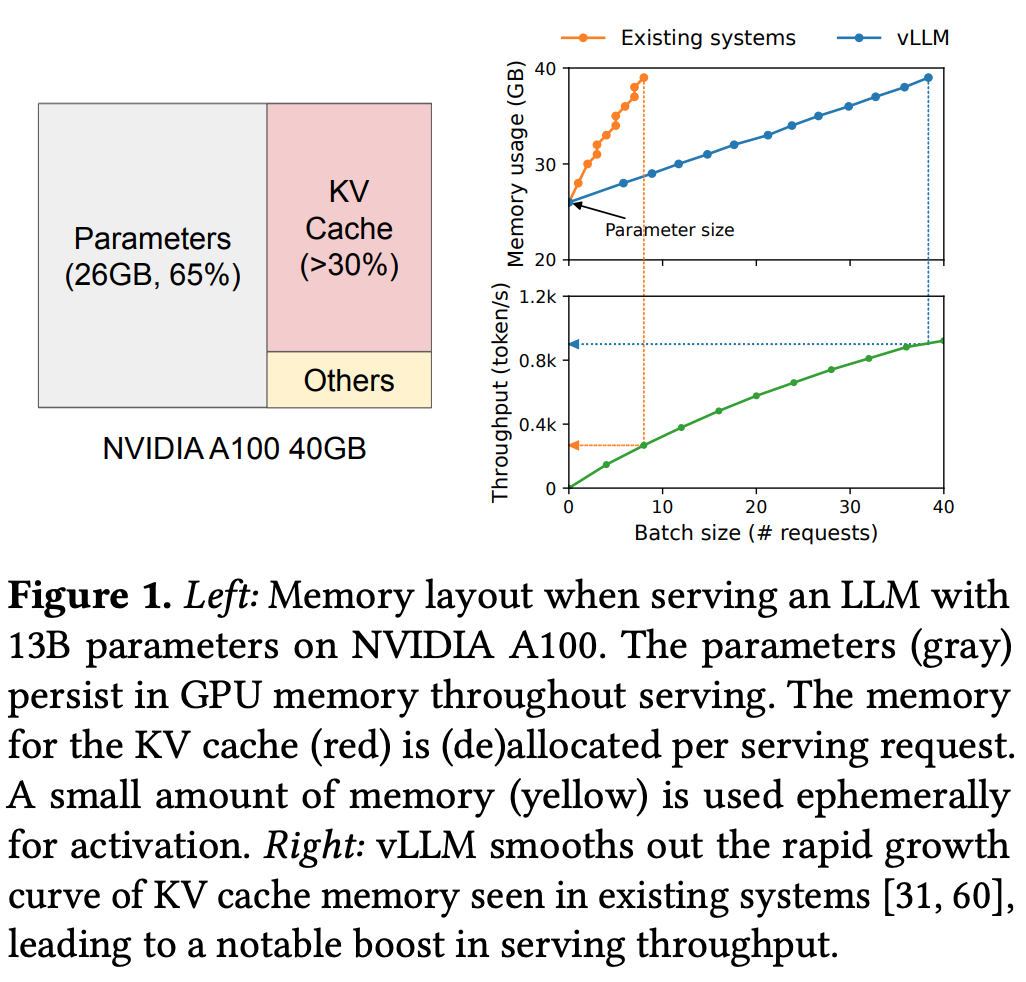
- 20.4% ~ 38.2% 의 KV cache memory 만 실제로 사용됨.
- Throughput 을 2~4배 향상
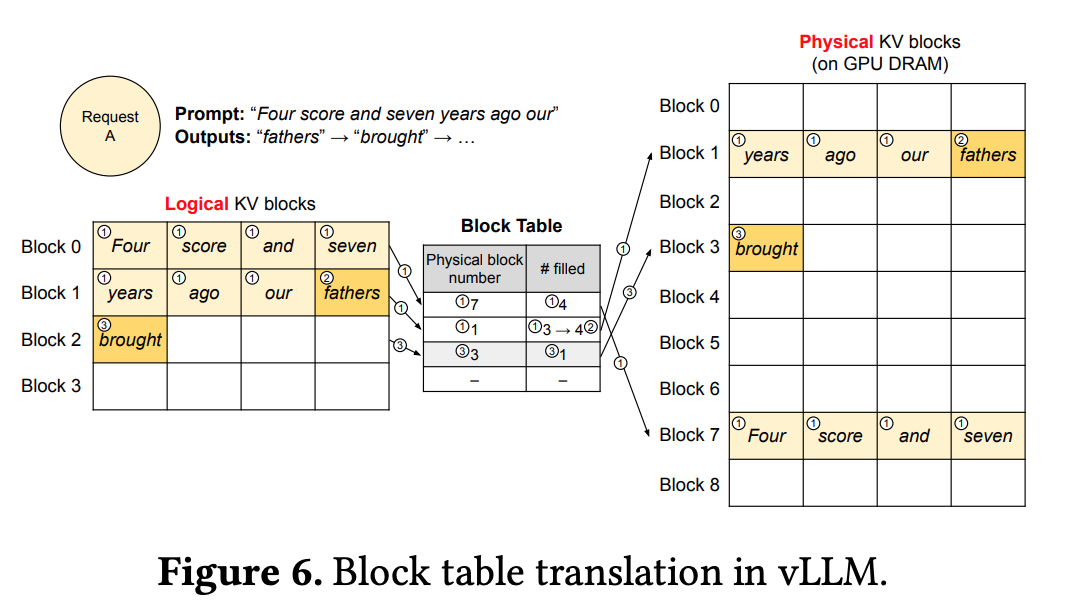
- PagedAttention: virtual memory 와 paging techniques 차용.
- OS 는 physical memory 를 fixed-sized page 로 나눈 뒤, logical page 로 mapping 함.
- Contiguous logical page 를 유지하면서 실제로는 non-contiguous physical memory pages 로 관리.
- key, value cache 를 non-contiguous 하게 관리하여 fragmentation 줄임.
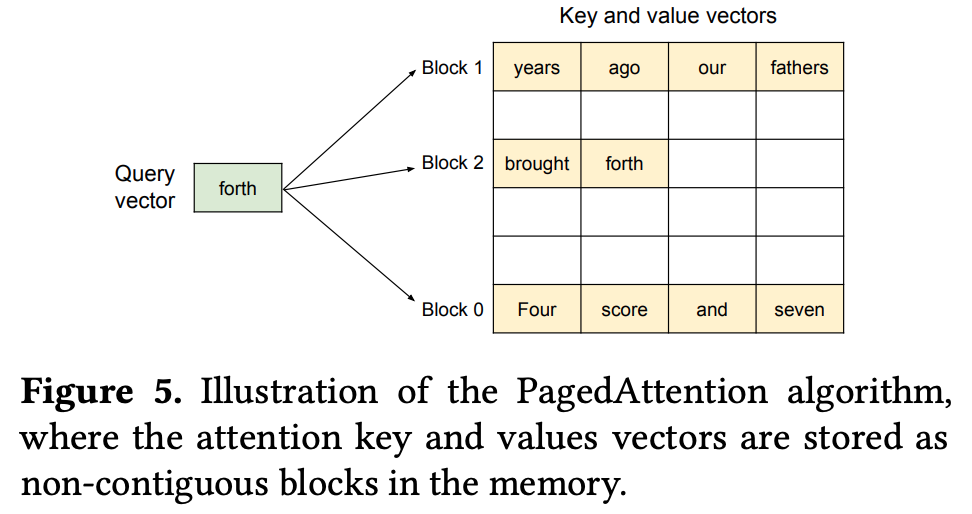
- 새로운 token 이 생성되면서 physical block number 와 # filled 가 업데이트 되어, 보다 효율적으로 GPU DRAM 을 활용할수 있음.
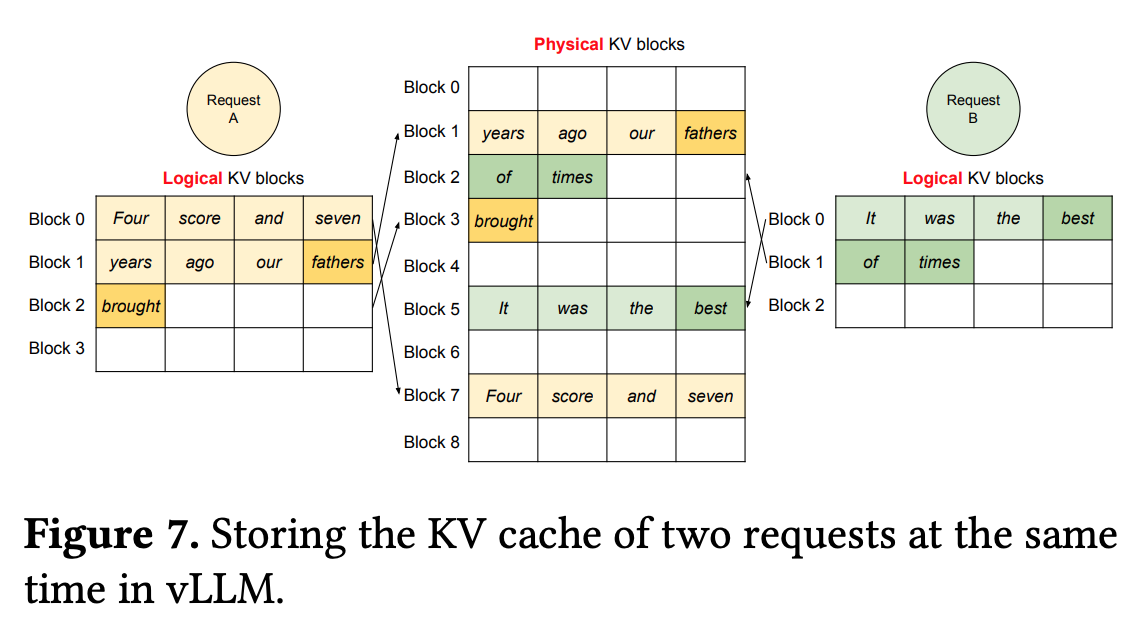
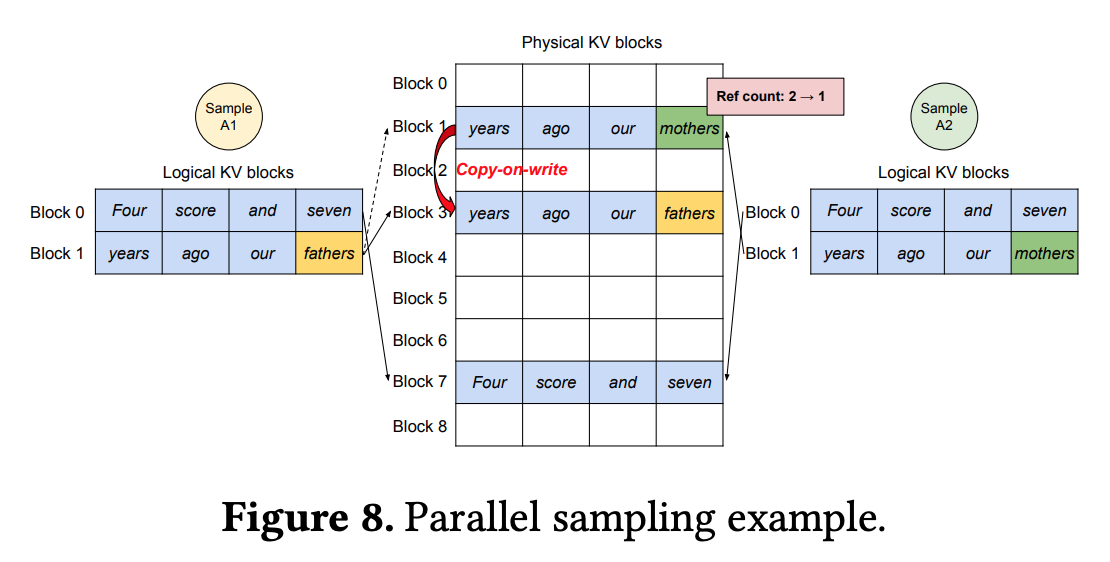
- parallel sampling
- physical memory -> logical memory 의 mapping 개수를 reference count 로 정의
- reference count 가 1 보다 클 경우, copy-on-write technique (OS 에서 folk 시 메모리 복사) 방식으로 새로운 physical memory block 에 복사후, reference count 를 -1
- reference count 가 1인 경우, 같은 block 에 저장
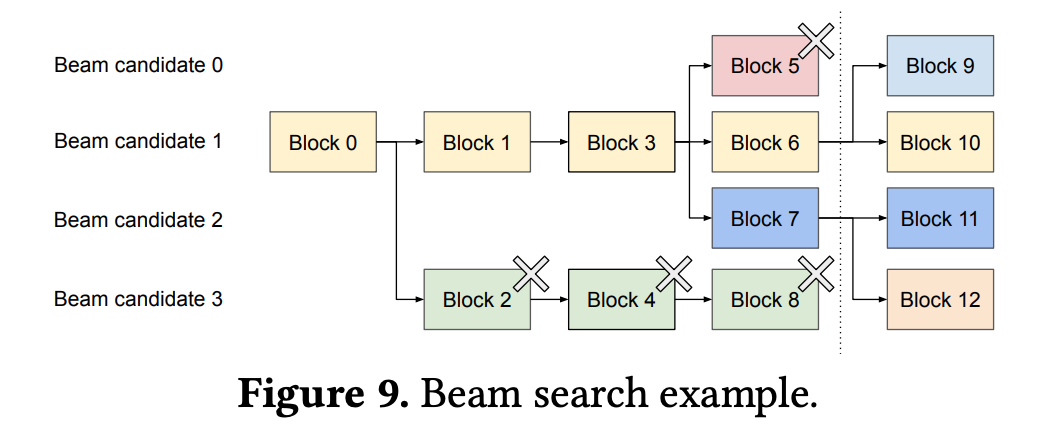
- beam search
- beam 개수 만큼 sequence 를 유지하면서 digress 되는 경우, block 을 새로 생성
- beam 에서 제거된 sequence 의 KV-cache 를 저장한 block 은 reference count 를 줄임
- reference count 가 0 이 되면 free.