(논문 요약) How much do language models memorize? (Paper)
핵심 내용
- unintended memorization: 데이터 셋 자체를 외운 것
- generalization: 데이터 생성 process 를 파악한 것
Formulation
- Entire memorization: 모델이 데이터를 설명하는 정보량
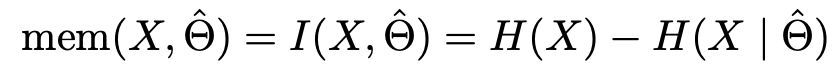
- Unintended memorization: 데이터 생성 프로세스를 알고 있을 때보다 더 감소된 정보량
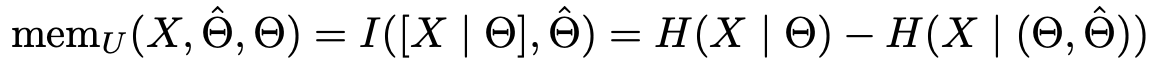
- Generalization: Entire memorization - Uninted memorization
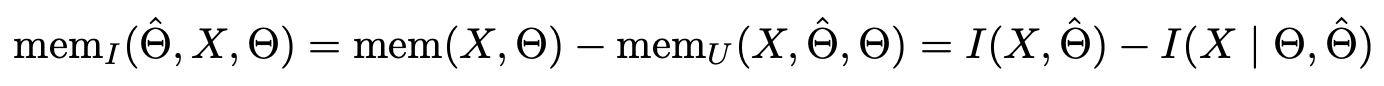
- Kolmogorov complexity
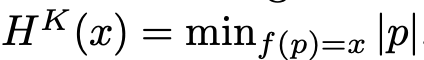
- Kolmogorov complexity of $x$ relative to another string $\theta$
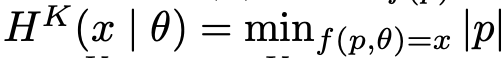
- Kolmogorov mutual information
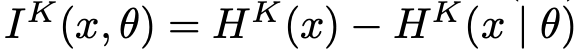
- Kolmogorov memorization
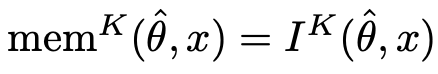 를 가정하면, 다음이 성립함.
를 가정하면, 다음이 성립함.
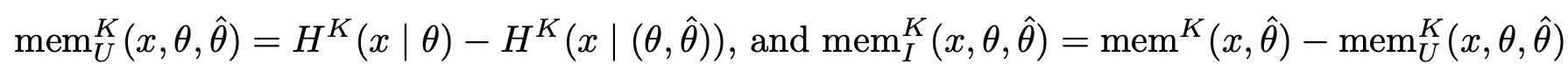
- Approximation
- $\hat{\theta}$ 는 target 모델, $\theta$ 는 oracle (실험에 쓰인 모델중 큰 모델)
- $H^K(x|\hat{\theta})$ 는 $p(x|\hat{\theta})$ 를 이용하여 계산
- $H^K(x|\hat{\theta}, \theta)$ 는$\max(p(x|\hat{\theta}), p(x|\theta))$ 를 이용하여 계산
- Model capacity: 모델이 saturation 까지 학습할수 있는 데이터 사이즈
실험 세팅
- GPT-2 architecture
- layer 1개~8개
- hidden dimension (32~512)
- param: 100K~20M
- training hyperparams
- $10^6$ training steps
- batch size: 2048
- Adam optimizer
- Data
- vocabulary size: 2048
- random sequence
- sequence length: 64
Bit-per-parameter for transformers
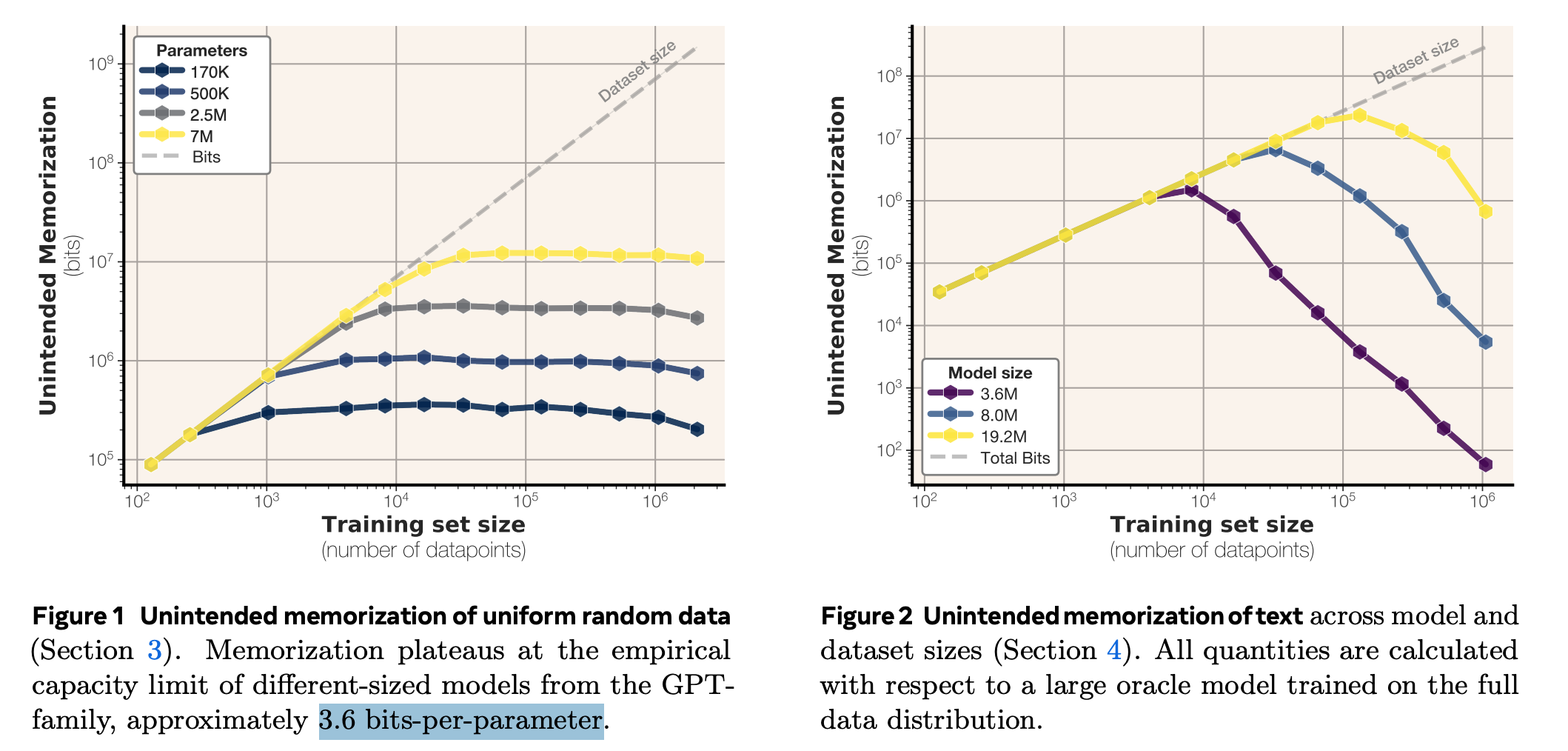
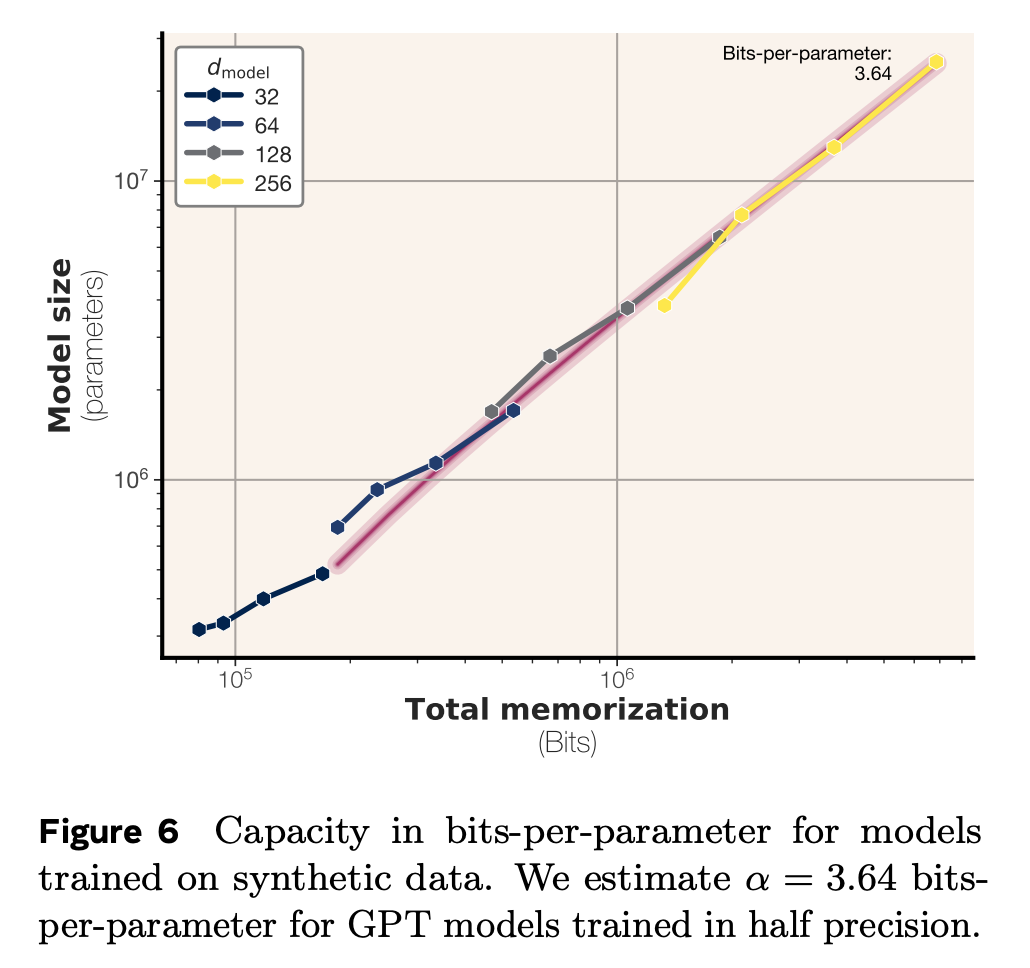
- bf16 에서 fp32 로 바꿔서 실험시, bits-per-parameter 가 3.51 에서 3.83 로 (10% 정도) 증가했다고함 (용량은 2배 늘었음에도 불구하고).
Double descent