Booting sequence
Firmware → Bootloader → Kernel → systemd → User Session
1️⃣ Power-On and Firmware Initialization
- Pressing the Power button → motherboard signals PSU.
- CPU resets registers and jumps to firmware (BIOS/UEFI).
- Firmware performs POST, detects hardware, and finds a bootable device.
2️⃣ Bootloader (e.g. GRUB)
- Loads the Linux kernel (
vmlinuz) andinitramfs. - Passes kernel parameters and jumps to the kernel entry point.
3️⃣ Kernel Initialization
- Architecture-specific setup (modes, page tables, stacks).
- Calls
start_kernel()— initializes memory, scheduler, devices, filesystems. - Finally launches the first userspace process (
/sbin/initorsystemd).
4️⃣ User Space Initialization
systemd(now standard) starts background services, mounts filesystems, and manages targets.
misc in linux kernel
subsystems
- Process Management
- Memory Management
- File Systems
- I/O Subsystems
- Networking
- Device Drivers
- Security Subsystems
- Inter-Process Communication (IPC)
- Kernel Timers and Clocks
- Virtualization and Containers
- Power Management
- Debugging and Tracing
- Kernel Modules and Loadable Subsystems
- Input/Output Scheduling
- Filesystem Caching and Buffers
kernel-space queue
- Workqueue
- Softirq queue
- Tasklet queue
- Timer queue
- RCU (read-copy-update) callback queue
- kthread worker queue – queues work specifically for custom kernel threads created by subsystems.
kernel-space daemon
| Kernel Thread | Purpose |
|---|---|
| ksoftirqd/n | Processes deferred softirqs when immediate execution would take too long. |
| kworker/n:m | Handles workqueue items in process context. |
| kswapd/n | Manages page reclaiming and memory swapping. |
| ksmd | Kernel Samepage Merging (memory deduplication). |
| kthreadd | The parent of all kernel threads. |
| irq/CPU-n | Handles per-CPU interrupts. |
Kernel Threads
- Exist only in kernel space and do not have a user-space address space (mm = NULL).
- Are schedulable and preemptible like user processes.
- kthread != kernel thread
- kthread are kernel threads that use the kthread_*() API such as kthread_create(), kthread_run(), kthread_stop(), kthread_should_stop()
Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA)
- Each NUMA node has its own set of processors and directly attached local memory.
- A processor can access its local memory much faster than it can access memory located on a remote NUMA node (non-local memory)
misc
- ‘volatile’ keyword: have compiler read from and write to the variable’s memory location directly every time, without optimizing (such as register caching).
- system cache line: A fixed-size memory block used during data transfer RAM ↔ cache.
- process states in top command
- R: Running or Runnable
- S: Interruptible Sleep
- D: Uninterruptible Sleep (waiting for I/O to complete)
- Z: Zombie - terminated, but its parent process has not yet called the wait() system call to collect its exit status and release its resources
- T: Stopped - suspended by a job control signal (like SIGSTOP, SIGTSTP, SIGTTIN, or SIGTTOU)
- t: Tracing Stop - stopped by a debugger (e.g., gdb)
- X: Dead - about to be completely removed from memory
Chapter 1 Introduction to the Linux Kernel
Interaction: user → C library (glibc) → system call → kernel → hardware
- printf() (in C library): performs formatting and buffering; internally uses the write() system call to output to a file descriptor.
- open() (in C library): mostly a thin wrapper around the open() or openat() system call.
- strcpy() (in C library): pure memory operation — does not make a system call (operates entirely in user space).
- Modern Linux uses vDSO (virtual dynamic shared object) to accelerate some system calls (e.g., gettimeofday(), clock_gettime()), allowing certain kernel services to be accessed without a full context switch.
A processor is always executing one of three types of code:
- user space
- kernel space (process context)
- kernel space (interrupt context)
Process & Thread
- Process: independent execution context
- Has its own virtual memory space, open file table, stack, heap, and CPU state.
- Each process is represented by a task_struct in the kernel.
- Thread: lightweight execution unit within a process
- Threads within the same process share memory and most resources (e.g., file descriptors, address space).
- Each thread has its own execution context (separate stack and CPU registers).
- A process always has at least one thread (the main thread).
- Implementations in Linux
- In Linux, threads are implemented as tasks—the same structure as processes.
- Threads are created using the clone() system call, which allows fine-grained control over what is shared (memory, file descriptors, etc.).
- Each thread has its own task_struct, but threads belonging to the same process share the same thread group ID (TGID).
Kernel Architecture
- Linux: monolithic kernel with modular design (loadable kernel modules).
- Core kernel runs in a single address space but supports dynamically loadable modules (e.g., device drivers).
- Uses preemption and fine-grained locking for scalability in modern SMP systems.
- Windows: hybrid kernel (not a true microkernel).
- Combines monolithic performance with microkernel modularity — kernel, executive, and drivers run in kernel mode.
Chapter 2 Getting Started with the Kernel
Kernel Source Tree (dirname:role)
- arch: Architecture-specific source
- block: Block I/O layer
- crypto: Crypto API
- Documentation: Kernel source documentation
- drivers: Device drivers
- firmware: Device firmware needed to use certain drivers
- fs: The VFS and the individual filesystems
- include: Kernel headers
- init: Kernel boot and initialization
- ipc: Interprocess communication code
- kernel: Core subsystems, such as the scheduler
- lib: Helper routines
- mm: Memory management subsystem and the VM
- net: Networking subsystem
- samples: Sample, demonstrative code
- scripts: Scripts used to build the kernel
- security: Linux Security Module
- sound: Sound subsystem
- usr: Early user-space code (called initramfs)
- tools: Tools helpful for developing Linux
Characteristics of Linux Kernel Code
- Cannot use the standard C library (libc) or standard user-space headers.
- Kernel code runs in a separate environment from user space and must use kernel-provided equivalents instead.
- Written in GNU C (a variant of C with GNU extensions).
- Most kernel code is written in GNU C, with limited use of assembly where necessary.
- Runs in a protected memory space (kernel space).
- Unlike user processes, kernel code has full access to system memory but is isolated from user space via hardware-enforced memory protection.
- Floating-point operations are strongly discouraged.
- The kernel avoids using the floating-point unit (FPU) because saving and restoring FPU state adds overhead and can disrupt user-space FPU usage.
- Each kernel thread or process has a small, fixed-size kernel stack.
- Typically 16 KB on 64-bit systems (and 8 KB on older 32-bit ones), which limits deep recursion and large local variables.
- Concurrency and synchronization are critical concerns.
- Kernel code often runs in parallel on multiple CPUs and must use proper locking mechanisms (e.g., spinlocks, mutexes, RCU).
- Portability must be maintained across different architectures.
- Kernel code should be architecture-independent where possible, using abstraction layers and standardized APIs.
Chapter 3 Process Management
Each process has:
- A unique program counter
- A process stack
- A set of CPU registers
Process Creation (fork())
- New processes are created using the fork() system call.
- Every process has one parent.
- All processes ultimately descend from init (PID 1) in older systems, or systemd (PID 1) in modern Linux.
- The process descriptor of the initial process is stored at the statically allocated address init_task.
- Return values:
- Parent receives the child’s PID.
- Child receives 0.
Process Termination (exit())
- A process terminates via the exit() system call:
- Its resources (memory, file descriptors, etc.) are freed.
- The process enters the EXIT_ZOMBIE state.
- A SIGCHLD signal is sent to its parent.
- Its child processes are re-parented to the parent process, or to init / systemd if the parent no longer exists.
Process Descriptor List
- All process descriptors are maintained in a doubly linked list.
- Each descriptor is a task_struct, containing fields such as state, priority, and PID.
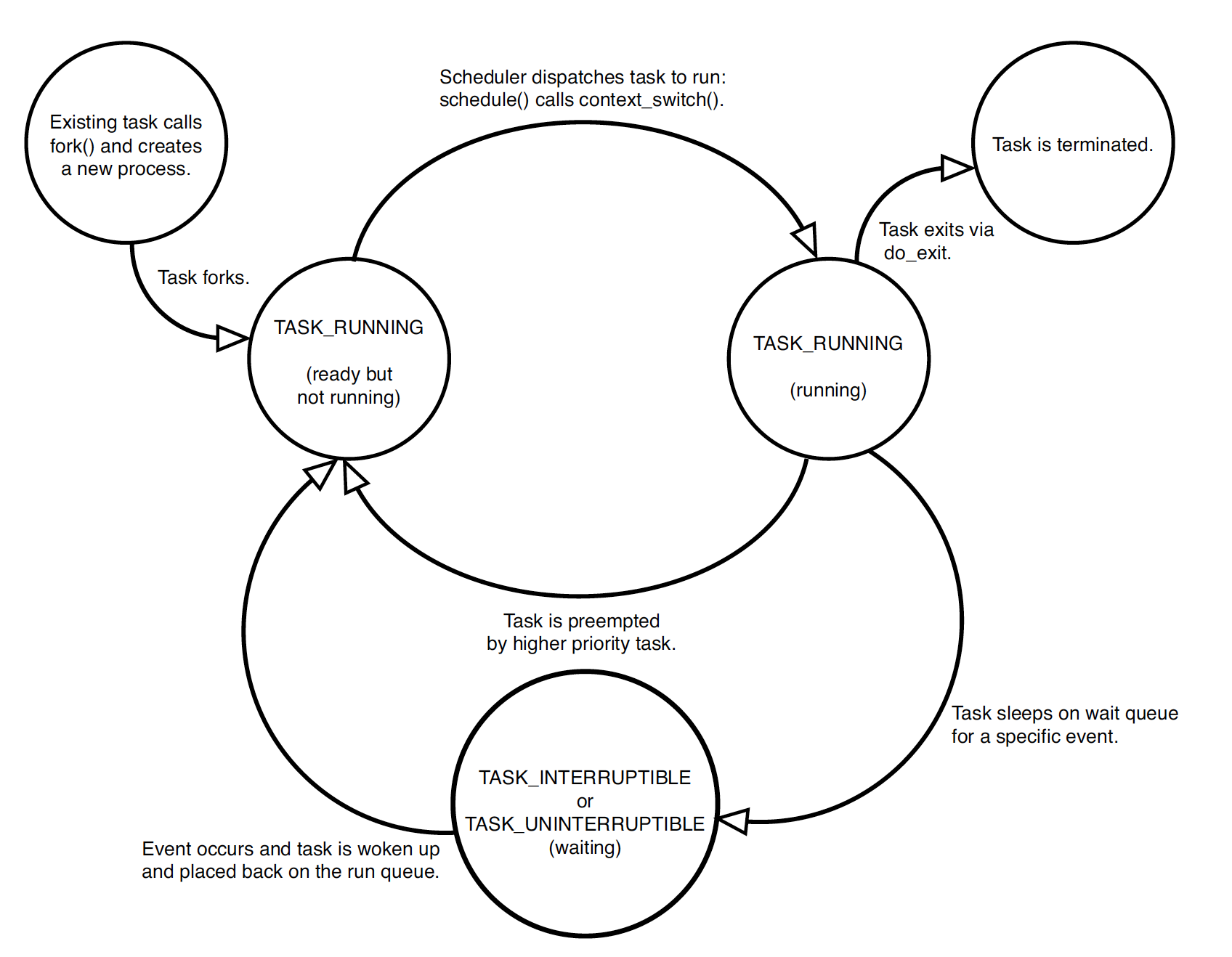
Process States and Sleep
- When a process sleeps, its state is set to:
- TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE (can wake on signals) or
- TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE (cannot wake on signals).
- Sleeping processes are placed into a wait queue.
Copy-on-Write (COW) in fork()
- After fork(), parent and child share the same physical memory pages.
- Both page tables are marked read-only.
- When either writes to a shared page, a page fault occurs, and the kernel allocates a new private copy for that process.
Chapter 4 Process Scheduling
real-time processes vs. normal processes
| Scheduler class | Typical policies | Priority range (the lower, the more priority) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real-time (RT) | SCHED_FIFO, SCHED_RR | 1–99 | rt_priority 가 높은 것이 항상 먼저 실행됨 |
| CFS (fair) | SCHED_OTHER, SCHED_BATCH, SCHED_IDLE | 100–139 (user-space nice = –20 to +19) | weight = $1024 / 1.25^{nice}$ 에 비례하여 time-slice 배정 |
CFS (Completely Fair Scheduler)
- The scheduler always runs the process with the smallest vruntime, which represents how much CPU time the task has used relative to its weight (priority/niceness).
- All runnable tasks are stored in a red-black tree, ordered by vruntime; the leftmost node (least vruntime) is selected to run next.
- When a task calls a blocking function (e.g., read() on an empty pipe or futex_wait()), it is removed from the red-black tree and added to the corresponding wait queue (e.g., I/O wait queue, futex wait queue).
- When the event that the task was waiting for occurs (e.g., I/O completion, lock release, timer expiration), the task is moved from the wait queue back to the red-black tree, making it runnable again.
Time-slice calculation during equal-weighting with CFS
| Runnable tasks | Time slice per task | Effective latency (config) |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 24 ms | 48 ms |
| 4 | 12 ms | 48 ms |
| 8 | 6 ms | 48 ms |
| 16 | 6 ms (min reached) | 96 ms (16×6ms) |
| 32 | 6 ms (min reached) | 192 ms (32×6ms) |
schedule() and Context Switching
- The schedule() function decides the next task to run.
- A context switch occurs via context_switch(), which:
- Saves the current task’s CPU registers and kernel stack pointer.
- Loads the next task’s saved state and updates CPU context accordingly.
- On modern kernels, context switches are optimized with lazy FPU saving and NUMA-aware scheduling.
- Lazy FPU saving defers the expensive process of saving and restoring the state of the Floating Point Unit (FPU) registers until it is absolutely necessary
- NUMA-aware scheduler ensures that all the resources requested by a performance-critical application are available within a single NUMA zone.
Chapter 5 System Calls
user-space ↔ c library (glibc, musl) ↔ system call interface ↔ system call handler ↔ kernel implementation
System Call Table
- The sys_call_table contains pointers to system call handler functions, indexed by their system call numbers.
- In modern kernels, this table is architecture-specific and generally not exported to modules for security and stability reasons.
User-space and Kernel-space Memory
- User-space and kernel-space memory are strictly separated for protection and stability.
- The kernel must use special helper functions to safely copy data between these spaces:
- copy_from_user() — copies data from user space to kernel space.
- copy_to_user() — copies data from kernel space to user space.
- These functions perform access checks to prevent invalid memory references and ensure kernel safety.
Chapter 7 Interrupts and Interrupt Handlers
Terminology
- IRQ (Interrupt Request): A signal sent by hardware to request CPU attention.
- ISR (Interrupt Service Routine): Function executed in response to an interrupt.
- IDT (Interrupt Descriptor Table): Table mapping interrupt vectors to their handlers.
- APIC (Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller)
- MSI (Message-Signaled Interrupts)
- Interrupt vector: index used by the CPU to know which handler to run when an interrupt arrives.
Interrupt Flow
- Hardware → electrical signal → interrupt controller (e.g., APIC) → IRQ → CPU → IDT → kernel interrupt entry → registered interrupt handler (driver ISR) → return to normal execution
Interrupt Context
- Executed independently of any process context (no associated user process).
- No blocking or sleeping is allowed.
- Used for immediate, time-critical handling.
Top Half
- Runs immediately when the interrupt occurs.
- Handles urgent tasks, such as acknowledging or clearing the interrupt and reading device state.
- Runs in interrupt context (atomic, cannot sleep).
- Must complete quickly to minimize interrupt latency.
Bottom Half
- Runs after the top half completes.
- Handles deferred work, such as data processing or notifying waiting processes.
- Implemented using softirqs or workqueues in modern Linux.
Driver and Interrupt Management
- On driver load: request_irq() registers an ISR for a given IRQ.
- On driver unload: free_irq() releases the IRQ line.
- Modern drivers may also use devm_request_irq() for automatic resource management.
Shared Interrupt Lines
- Multiple devices can share a single IRQ line.
- When an interrupt occurs, all registered handlers for that IRQ are called.
- Each handler checks its device status register to confirm the source.
- If not responsible, the handler returns IRQ_NONE.
Interrupt Disabling
- Interrupts may be disabled temporarily:
- During the top half of interrupt handling.
- While accessing critical kernel data or performing atomic operations.
- During context switches or scheduler operations.
- Via calls such as local_irq_disable(), spin_lock_irqsave(), or similar primitives.
- The kernel automatically re-enables interrupts when safe to do so, and modern kernels minimize interrupt disabling to reduce latency.
Interrupt Masking
- When an interrupt is received, the kernel (via the interrupt controller) may mask or disable the interrupt temporarily to prevent repeated interrupts from the same device until it is fully serviced.
- MSI (Message-Signaled Interrupts)
- The device writes a small message to a specific memory-mapped address (MSI address).
- The message is then translated by the PCIe controller/APIC into an interrupt vector for the CPU.
- Devices will not send another MSI message for that vector until the previous interrupt is fully handled.
Chapter 8 Bottom Halves and Deferring Work
| Mechanism | Runs in | Concurrency | Use for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Softirq | Interrupt context | Can run on multiple CPUs concurrently (each CPU handles its own) | High-frequency, time-critical kernel tasks (e.g., networking, block I/O) |
| Workqueue | Process context (kernel thread) | Can sleep/block; multiple worker threads may run in parallel | Deferred work that can sleep or perform blocking operations (e.g., memory allocation, file I/O) |
SoftIRQ
- A type of bottom-half mechanism used for high-performance, low-latency tasks (e.g., networking).
- Executes in interrupt context, so it cannot sleep or block.
- SoftIRQs do not preempt other softirqs running on the same CPU.
- Usually marked as pending by an interrupt handler.
- Only a few subsystems directly use softirqs today:
- Networking (NET_RX_SOFTIRQ, NET_TX_SOFTIRQ)
- Block I/O (BLOCK_SOFTIRQ)
Workqueue
- Used when the deferred task may sleep or requires operations such as:
- Allocating large memory regions
- Acquiring semaphores or mutexes
- Performing blocking I/O
- Each workqueue maintains one or more worker threads that execute queued work items in process context.
- Modern kernels (since 2.6 and later) use unified workqueues (system_wq, system_highpri_wq, etc.) shared across subsystems for efficiency.
ksoftirqd
- A per-CPU kernel thread that runs softirqs in process context, allowing scheduling and sleeping.
- Prevents softirqs from monopolizing CPU time.
- Typically, one ksoftirqd/
thread exists per CPU.
Chapter 9 An Introduction to Kernel Synchronization
Concurrency Concepts in Modern Linux
- Critical region: A section of code or data that must be accessed by only one thread or process at a time to maintain consistency.
- Race condition: A situation where multiple threads or processes access and modify shared data concurrently, and the final outcome depends on the timing of their execution.
- Atomic operation: An operation that completes entirely without being interrupted. In Linux, atomic operations are typically implemented using CPU instructions such as atomic_add(), cmpxchg(), or xchg().
- Contention: A state in which a lock is already held by one thread or process, forcing others to wait until it is released.
When race conditions occur?
- If a critical region is protected using atomic operations or proper locking mechanisms (e.g., spinlocks, mutexes), race conditions do not occur.
- Conversely, if a critical region is interrupted or accessed by another thread without synchronization, a race condition arises.
Common Deadlock Prevention Techniques
- Disable local interrupts when acquiring a spinlock (common in kernel-level code) to prevent preemption during lock acquisition.
- Lock ordering: Always acquire multiple locks in a consistent global order to avoid circular dependencies. Modern Linux uses lockdep to detect violations dynamically.
- Avoid double-acquisition: Never attempt to acquire the same lock twice in the same thread without releasing it first.
Chapter 10 Kernel Synchronization Methods
Blocking vs. Spinning
- Blocking: When a process or thread cannot proceed until a condition is met, the scheduler puts it into a sleeping state and switches to other runnable tasks.
- Spinning: A thread repeatedly checks (busy-waits) for a lock to become available, consuming CPU time. Used in spinlocks, typically within interrupt context or very short critical sections where sleeping is not allowed.
Example: Spinlock
spinlock_t mr_lock;
spin_lock(&mr_lock);
/* critical section ... */
spin_unlock(&mr_lock);
Semaphore
- Binary semaphore: allows one thread at a time (similar to a mutex).
- Counting semaphore: allows multiple concurrent holders.
- Down operation: (down(), down_interruptible(), or down_killable()) — attempts to acquire; if count is 0, the task sleeps in the wait queue.
- Up operation: (up()) — releases the semaphore and wakes one waiting task.
Example: Semaphore
/* define and initialize a semaphore named mr_sem with a count of one */
static DEFINE_SEMAPHORE(mr_sem);
/* attempt to acquire the semaphore (sleep if unavailable) */
if (down_interruptible(&mr_sem)) {
/* interrupted by a signal before acquisition */
}
/* critical section ... */
/* release the semaphore */
up(&mr_sem);
| Feature | Spinlock | Semaphore |
|---|---|---|
| Sleep allowed? | ❌ No (busy-waits) | ✅ Yes |
| Context | Used in atomic/interrupt context | Used in process context |
| Use case | Very short critical sections | Longer waits or shared resources |
| Overhead | Low (no context switch) | Higher (can block & wake up) |
| Concurrency | Only one holder (no queue) | Can have queue of waiters |
| Performance | Best for short locks | Better for long operations |
| Feature | Binary Semaphore | Mutex |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Generic signaling (not always ownership-based) | Designed for mutual exclusion (lock/unlock by same thread) |
| Context | Used in process context | Used in process context |
| Ownership | No ownership — any thread can up/down | Has ownership — only the locker can unlock |
| Priority inheritance | ❌ Not supported | ✅ Supported (prevents priority inversion) |
| Usage safety | Easier to misuse | Safer and simpler for locking |
| Common use | Synchronization between tasks | Protecting shared data (critical sections) |
Read/Write Locks
- Reader lock: shared; multiple readers can hold it simultaneously.
- Writer lock: exclusive; only one writer at a time.
- Implemented using rwlock_t (for spin-based locks) or rw_semaphore (for sleepable locks).
| Feature | rwlock_t (spinlock) | rw_semaphore |
|---|---|---|
| Sleep allowed? | ❌ No (busy-wait) | ✅ Yes (can block) |
| Context | Atomic / interrupt context | Process context only |
| Best for | Short critical sections | Long operations (e.g. disk I/O, file access) |
| Performance | Low latency, no sleep | Can sleep, less CPU usage when waiting |
Sequence Locks (Seqlocks)
- Designed for data that is read frequently but rarely written.
- Writers are never starved, but readers may retry if a write occurs during reading.
- e.g. timekeeping (xtime), VDSO data, and networking stats
Chapter 11 Timers and Time Management
| Hardware | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| TSC (Time Stamp Counter) | A counter in each CPU core that increments every CPU cycle. | High-resolution, fast timing source. Used for fine-grained timestamps. |
| HPET (High Precision Event Timer) | A separate hardware timer chip with nanosecond precision. | Used for system clock, scheduling, and timekeeping if available. |
| APIC timer (Local/IO-APIC) | Per-CPU timer used for generating periodic interrupts. | Used for task scheduling and time slicing. |
| RTC (Real-Time Clock) | Battery-backed clock chip on motherboard. | Maintains wall-clock time across reboots. |
Timer Tick Mechanism:
- A periodic interrupt increments a global timer counter when ticks are enabled (historically, 1 ms interval for desktop and laptop).
- In tickless mode, the kernel stops these periodic ticks during idle periods and instead programs a hardware timer (e.g., HPET, Local APIC timer, or TSC-deadline timer) to generate the next wake-up event.
jiffies:
- A global variable representing the total number of timer ticks since system boot.
- It is still maintained even on tickless systems for compatibility.
Timers in the Kernel:
- Deferred work such as timer callbacks runs in the softirq context, specifically under TIMER_SOFTIRQ.
- A timer expires when the current jiffies value is equal to or greater than its expiration time (actual execution may be delayed slightly).
- Modern kernels also use hrtimers (high-resolution timers) for more precise scheduling.
Waiting in Drivers:
- Hardware drivers sometimes wait for device operations to complete.
- A simple busy-wait loop can be used with a timeout check (less efficient).
- The preferred approach is to call schedule_timeout() or wait_event_timeout() to sleep for a defined duration.
- These sleep functions must not be called in interrupt context.
Chapter 12 Memory Management
Memory Management Unit (MMU)
- The MMU (Memory Management Unit) translates virtual addresses to physical addresses using page tables.
- Translation occurs on a per-page basis, typically with 4 KB pages.
- Large and huge pages, such as 2 MB or 1 GB, are also supported on modern systems.
struct page
- Each physical page frame in memory is represented by a struct page in the kernel. It contains:
- flags — status bits (locked, dirty, referenced, etc.)
- reference count — number of mappings or users of the page
- mapping — pointer to the associated file or anonymous memory (via address_space or anon_vma)
- virtual address — kernel virtual address (if permanently mapped; not all pages are)
Page Fault
- A page fault occurs when a process accesses a virtual address not currently mapped in its page tables or when access permissions are violated.
- If the data exists in physical memory (but the page table is missing the entry), the kernel updates the page table and resumes the process.
- If the data must be read from swap space or a file (lazy loading), the kernel loads it, updates the page table, and resumes the process.
- If the process accesses an invalid or protected address, the kernel raises a segmentation fault (invalid page fault).
Memory Zones
- Physical memory pages are divided into zones for allocation constraints:
- ZONE_DMA – reserved for DMA-capable hardware (legacy devices)
- ZONE_NORMAL – directly mapped in the kernel’s virtual address space
- ZONE_HIGHMEM – used only on 32-bit systems; not permanently mapped
- Typical configurations:
- x86-32 (legacy):
- ZONE_DMA: < 16 MB
- ZONE_NORMAL: 16 – 896 MB
- ZONE_HIGHMEM: > 896 MB
- x86-64:
- No ZONE_HIGHMEM; all memory is directly mapped
- x86-32 (legacy):
Contiguous Memory
- Physically contiguous memory improves DMA and CPU access efficiency.
- kmalloc → physically & virtually contiguous
- vmalloc → virtually contiguous, but not physically contiguous
- Used for large kernel allocations (e.g., dynamically loaded modules, buffers)
- User-space malloc simply requests virtual memory via brk or mmap; it’s not physically contiguous.
SLUB
- kernel memory allocator in modern Linux for small, frequently used kernel objects.
- Each cache (e.g., kmalloc-64, task_struct) holds objects of one size/type.
- Each cache consists of multiple slabs, which are groups of contiguous pages divided into equal-size objects.
Chapter 13 The Virtual Filesystem
user space ↔ VFS ↔ filesystem (FAT, NTFS, ext4, etc) ↔ physical media
Core VFS Structures
- super_block
- Holds filesystem-wide metadata such as type, size, and status. It exists both in memory and on disk (as part of the filesystem’s metadata region).
- inode
- Represents individual files or directories and stores metadata (permissions, ownership, timestamps, size, etc.). Each inode usually has an on-disk representation and an in-memory cache.
- dentry (directory entry)
- Represents a single component in a pathname and links a name to its corresponding inode. Dentries exist only in memory and are managed by the dentry cache to speed up path lookup (e.g., /bin/vi has dentries for bin and vi).
- file
- Represents an open file instance. It holds references to a dentry and an inode and is created in memory by the open() system call and released by close().
A process’s file-related data structures are accessible through its task_struct:
- files_struct – Table of open file descriptors (FDs) for the process.
- fs_struct – Holds filesystem context such as the current working directory and root directory.
- nsproxy – References the namespaces the process belongs to (e.g., mount, PID, network, IPC).
Chapter 14 The Block I/O Layer
Linux Block I/O Overview
- Block device: A device that supports random access to fixed-size blocks (e.g., hard disks, SSDs, flash memory).
- Character device: A device that transfers data as a continuous stream (e.g., serial ports, keyboards, mice, printers).
- Sector: The smallest physical storage unit of a block device (typically 512 bytes or 4 KiB).
- Block (filesystem level): The smallest logical I/O unit used by the filesystem, typically a power-of-two multiple of the sector size.
- Segment: A contiguous range of blocks used within an I/O request.
I/O Request Structures
- struct bio: Represents a single block I/O request, composed of one or more segments.
- Contains an array of struct bio_vec elements.
- struct bio_vec describes a segment: (page, offset, len).
- Request queue:
- Filesystems and other kernel components enqueue I/O requests (struct request) to the queue.
- The device driver dequeues and submits them to the hardware.
- Each struct request may reference one or more struct bios.
I/O Schedulers (Legacy and Modern)
- I/O Scheduler: Optimizes performance by merging and ordering requests before dispatching to hardware.
- Merge: Combine adjacent I/O requests into a larger one.
- Sort: Order requests by physical sector to reduce seek time.
- Traditional Schedulers
- Deadline Scheduler: Prevents starvation by maintaining three queues (sorted, read FIFO, write FIFO).
- Typical expiration: reads ~500 ms, writes ~5 s.
- Prioritizes reads to reduce latency.
- Anticipatory Scheduler: Waits briefly (~6 ms) after a read, anticipating nearby read requests. (Removed since Linux 2.6.33)
- CFQ (Completely Fair Queuing): Assigns each process its own queue and services them in a round-robin fashion. (Replaced by BFQ and MQ-deadline in modern kernels)
- Noop Scheduler: Performs simple request merging only; useful for SSDs where seek optimization is irrelevant.
- Deadline Scheduler: Prevents starvation by maintaining three queues (sorted, read FIFO, write FIFO).
- Modern Schedulers (blk-mq era)
- MQ-Deadline: A multi-queue version of the deadline scheduler, suitable for modern multi-core systems.
- BFQ (Budget Fair Queuing): Provides fairness and throughput control, often used on desktop systems.
- None Scheduler: Disables scheduling, handing requests directly to the device (often optimal for high-performance SSDs and NVMe).
Chapter 15 The Process Address Space
Linux Process Memory Layout
- Each process has its own virtual address space, isolated from others.
- Threads within the same process share this address space (and thus the same memory mappings).
Memory Regions
- Text (code) segment: executable program instructions
- Data segment: initialized global and static variables
- BSS segment: uninitialized global/static variables (zero-filled at load time)
- Heap: dynamically allocated memory (e.g., via malloc())
- Stack: user-space stack for each thread
- Shared libraries: mapped regions for dynamically linked libraries (e.g., libc)
- Memory-mapped files: file contents mapped into memory via mmap()
- Shared memory segments: explicitly shared regions between processes (shmget, mmap, etc.)
- Anonymous mappings: non-file-backed regions (used by the heap, stacks, etc.)
struct mm_struct — Process Memory Descriptor
- Represents the entire virtual memory layout of a process.
- Key components include:
- Page tables: map virtual addresses to physical pages
- List/tree of VMAs (vm_area_struct): each describes one continuous mapped region
- Segment boundaries: start and end of code, data, heap, and stack
- Reference counters, locks, and statistics: e.g., resident set size, swap usage
struct vm_area_struct — Virtual Memory Area (VMA)
- Represents a contiguous region of memory with uniform properties:
- Start and end virtual addresses
- Access permissions (read, write, execute)
- Mapping flags and attributes
- Associated file (if file-backed) and offset
- Each mm_struct contains multiple VMAs, usually organized as a red-black tree for efficient lookup.
mmap() and munmap()
- mmap() creates mappings between files or devices and a process’s virtual memory.
- It can also allocate anonymous memory (when no file descriptor is specified).
- munmap() removes such mappings.
Page Table Structure (x86_64, 4-level paging)
- PGD: Page Global Directory (top-level)
- P4D: Page 4th-level Directory (often folded in older kernels)
- PMD: Page Middle Directory
- PTE: Page Table Entry (points to a physical page)
- Each struct page represents a physical page frame in memory.
TLB (Translation Lookaside Buffer)
- A hardware cache that stores recent virtual→physical translations.
- The CPU checks the TLB first.
- On a miss, it walks the page tables, retrieves the mapping, and updates the TLB automatically.
Chapter 16 The Page Cache and Page Writeback
Linux Page Cache and Writeback
- Page cache: Stores disk data in main memory to reduce disk I/O and speed up file access.
- Page writeback: When cached pages are modified, they are marked as dirty. The kernel periodically writes dirty pages back to disk in batches, managed by the writeback mechanism (flush-* kernel threads).
- Laptop mode: When enabled (/proc/sys/vm/laptop_mode), the kernel delays dirty page writeback to reduce disk activity and save battery power—especially useful for spinning disks.
Cache eviction
- LRU eviction: Least Recently Used pages are evicted first to free memory.
- Two-list strategy: The kernel maintains an active and an inactive LRU list. Pages that are frequently accessed are promoted to the active list, while less-used pages are demoted to the inactive list and eventually reclaimed.
struct address_space
- Represents the cache of a file in memory.
- Includes a pointer to the owner of the address space, usually the file system’s struct inode or a struct block_device.
- Includes a data structure (often an xarray) used to store pointers to the actual struct page objects that make up the page cache for this object, indexed by file offset.
Chapter 17 Devices and Modules
Device Types
- Block devices: Provide buffered access to data in fixed-size blocks (e.g., disks, SSDs). Accessed via files like /dev/sda.
- Character devices: Provide unbuffered, sequential access to data (e.g., serial ports, keyboards). Accessed via files like /dev/ttyS0.
- Network devices: Represent interfaces for packet-based communication (e.g., eth0, wlan0), managed through the kernel’s networking stack rather than the traditional device file interface.
Loadable Kernel Modules (LKM)
- LKMs can be dynamically loaded and unloaded into the running Linux kernel without rebooting, using tools like insmod, rmmod, or modprobe.
- module_init() registers the module’s initialization function (called when loaded).
- module_exit() registers the cleanup function (called when unloaded).
- Modern kernels often use the MODULE_LICENSE, MODULE_AUTHOR, and MODULE_DESCRIPTION macros for metadata.
- Kernel module parameters can be exposed and configured using module_param() or module_param_array().
Kernel Objects
- struct kobject: Core structure representing kernel objects.
- Includes members such as name, parent, kset, ktype, and reference count (kref).
- struct ktype: Defines shared behavior for a group of kobjects.
- Callbacks like release, sysfs_ops (read/write), and default_attrs.
- struct kset: Represents a collection of kobjects (e.g., all block devices).
- Each kset has its own subsystem and uevent operations.
Sysfs
- Sysfs is an in-memory virtual filesystem mounted at /sys, exposing kernel objects to user space.
- It maps kobjects to directory entries (dentries), allowing structured access to kernel attributes.
- Common top-level directories include /sys/block, /sys/bus, /sys/class, /sys/devices, /sys/kernel, /sys/module, and /sys/power.
- Sysfs allows user-space tools (like udev and systemd-udevd) to query and react to kernel state changes.
Kernel Events (Uevents)
- The Kernel Events Layer notifies user space of significant system events
- e.g., device addition/removal, disk changes, power events.
- An event includes:
- Source: The associated kobject and its sysfs path.
- Action: The event type (add, remove, change, etc.).
- Optional attributes: Extra key–value pairs from sysfs.
- Events are delivered via netlink sockets (specifically, the NETLINK_KOBJECT_UEVENT family).
- User-space daemons like udevd listen for these messages and handle them asynchronously (e.g., creating device nodes in /dev).
Chapter 18 Debugging
Requirements for Effective Kernel Debugging
- A well-defined and reproducible bug.
- Knowledge of the kernel version and configuration where the issue appears.
- Familiarity with the relevant subsystem or sufficient investigation skills (and sometimes luck).
Types of Bugs
- Common issues include logic errors, race conditions, and hardware mismanagement.
- These can lead to slow performance, crashes, or data corruption.
- Kernel developers typically start from visible symptoms (e.g., crashes, hangs) and work backward to identify root causes.
Using printk()
- During early boot, normal printk() may be unavailable; only early_printk() (architecture-dependent) can output messages.
- Kernel messages are logged via the ring buffer, accessible through /proc/kmsg, dmesg, or the journald system (systemd-journald) on modern Linux systems.
- Older systems used klogd and syslogd, which wrote messages to /var/log/messages.
Oops Messages
- An Oops occurs when the kernel detects an exception (e.g., null pointer dereference, illegal instruction).
- The kernel prints register contents, stack trace, and code location.
- Symbols can be decoded using kallsyms or analyzed via dmesg, gdb, or crash utilities.
- After an Oops, the affected process is usually terminated, but the system may remain partially functional.
Kernel Panic
- A kernel panic occurs when the kernel hits an unrecoverable error in a critical context (e.g., init, idle, or interrupt handlers).
- The system halts and displays a message like: Kernel panic – not syncing: Fatal exception
- If the fault happens in a non-critical context, only the offending process is killed, not the whole system.
Compile-Time Debugging Options
- Build-time flags such as CONFIG_DEBUG_SPINLOCK, CONFIG_DEBUG_ATOMIC_SLEEP, or CONFIG_DEBUG_SLAB help detect improper locking, memory misuse, or sleeping in atomic contexts.
Assertion and Debug Macros
- The kernel provides assertion-style macros to detect unexpected conditions:
- BUG(), BUG_ON(), WARN_ON(), BUILD_BUG_ON(), panic(), dump_stack().
- These macros are used to stop execution or log critical diagnostics when conditions fail.
Debuggers
- Static analysis: gdb vmlinux /proc/kcore allows inspection and disassembly of kernel memory and code (read-only, no breakpoints).
- Remote debugging: kgdb enables full source-level debugging by connecting a debug host to a target machine running the kernel, supporting breakpoints, variable inspection, and single-stepping.
- Modern tools like crash, drgn, and bpftrace can also assist with live or post-mortem kernel debugging.
Chapter 19 Portability
Word Size
- Word size: the amount of data a machine can process in a single operation (e.g., 64-bit CPU).
- Typically equals the size of a general-purpose register (GPR), but this can vary on some architectures (e.g., ARM may have mixed register sizes).
Opaque Types
- Opaque types have their internal structure and implementation details hidden.
- Do not assume their size or representation.
- Examples: pid_t, uid_t, gid_t, dev_t, atomic_t, size_t, etc.
Notes and Best Practices
- Some kernel variables must use specific types — for example, interrupt flags should be of type unsigned long.
- Use exact-width integer types for hardware, networking, and binary data: u8, u16, u32, u64 and their signed variants.
- Always distinguish between signed char and unsigned char; they are not interchangeable.
- Respect natural alignment and use padding properly to avoid performance issues or misalignment faults.
- Never assume endianness; use conversion macros such as cpu_to_le32(), le32_to_cpu(), etc.
- Use the HZ constant for time conversions (e.g., jiffies to seconds) instead of assuming a fixed tick rate.
- Do not hardcode page size; use PAGE_SIZE, which varies by architecture and configuration.
- Some architectures have weak memory ordering — use appropriate memory barriers (mb(), rmb(), wmb()) when needed.
- Ensure code is SMP-safe, preemption-safe, and supports high memory where applicable.
- In modern kernels, prefer using type-safe helper APIs (e.g., ktime_get(), atomic64_t, refcount_t) instead of raw integer manipulation.